Introduction: Why Custom Fragrance Development Matters
Custom fragrance development has become one of the most influential drivers of product differentiation in the home‑fragrance category. In markets across North America, Europe, and Oceania, consumers increasingly associate scent identity with brand personality, emotional value, and lifestyle positioning. Wax melts—due to their fast diffusion rate and relatively low barrier to entry—have rapidly become the testing ground for retailers and private‑label brands that plan to launch a larger fragrance portfolio.
Unlike standard off‑the‑shelf scents, custom fragrance matching allows brands to replicate a signature scent, refine an existing direction, or build an entirely new formula tailored to their market. Melt wax, with its high surface area when melted, offers excellent cold‑throw and hot‑throw performance, making it ideal for early‑stage testing before candle production.
This article provides a detailed, step‑by‑step explanation of how OEM fragrance matching is developed specifically for melt wax products—from initial request through pilot batch validation and market launch.
1. Typical Motivation for Custom Fragrance Matching
Brands pursue custom fragrance development for multiple reasons:
- They want a recognizable scent that sets their brand apart.
- They already have a candle scent and want matching melt wax SKUs.
- They need a fragrance that better represents a regional market preference.
- They wish to reformulate an existing scent due to compliance updates.
A strong signature scent contributes to:
- Higher repurchase cycles
- Clearer brand perception
- Emotional recall
- Seasonal or thematic storytelling
Studies show that scent‑based loyalty is significantly stronger in home‑fragrance categories than in general commodity products. When customers fall in love with a smell, they rarely switch brands immediately, especially when labeling and sensory memories are embedded in seasonal rituals.
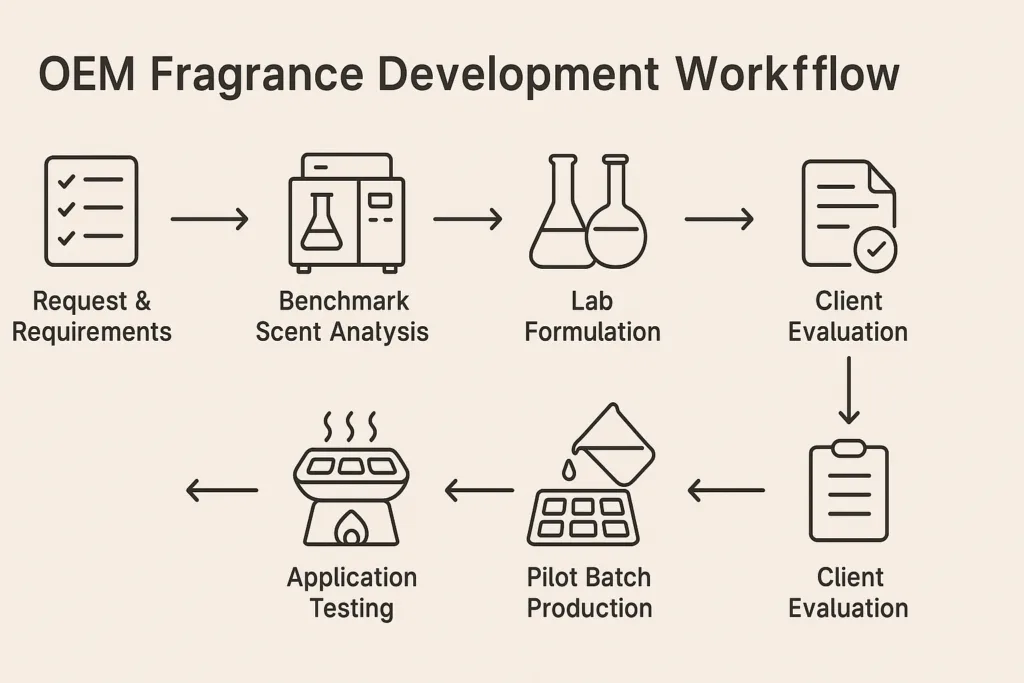
2. The Full OEM Flow for Melt Wax Fragrance Development
The OEM workflow for developing a custom scent includes several systematic stages.
Step 1 — Requirement Collection
Brands typically provide:
- Target aroma direction (fresh/woody/floral/gourmand/etc.)
- Benchmark product images, links, or samples
- Intended use category (wax melts vs candles)
- Packaging design plan
- Target regions and compliance requirements
If a customer already has an existing scent that needs reproduction, physical samples greatly improve accuracy.
The brand also shares expected positioning:
- Mass‑market
- Boutique retail
- Luxury premium line
This stage usually ends with a documented fragrance brief.
Step 2 — Benchmark Scent Analysis and Interpretation
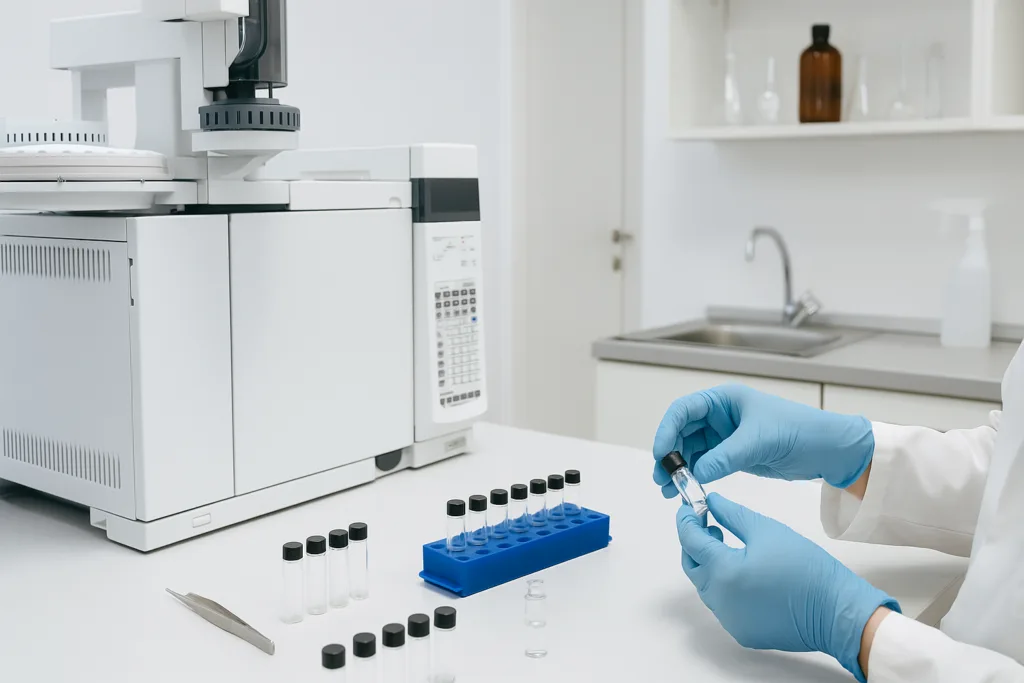
When reproduction is needed, chemists start with sensory evaluation and GC–MS (gas chromatography–mass spectrometry) testing.
GC–MS reveals:
- Volatile molecular structures
- Top‑note evaporation curve
- Solubility‑sensitive components
The laboratory typically reads:
- Citrus components
- Floral esters
- Synthetic modifiers
- Base fixatives
However, GC–MS alone does not complete the replication. The interpretative stage relies on trained evaluators who understand how notes behave when mixed with melt‑wax formulations.
Step 3 — Prototype Fragrance Composition
Multiple trial formulas are developed based on three evaluation criteria:
- Top Note and Immediate Impression – perceived during the first 3 seconds
- Mid‑Note Stability – maintains presence after heating
- Base Fixative Persistence – stays after cooling
The first prototype may be:
- Slightly sharper than the original scent
- Wet and sweet at top
- Soft or woody after cooling
Application tests start here.
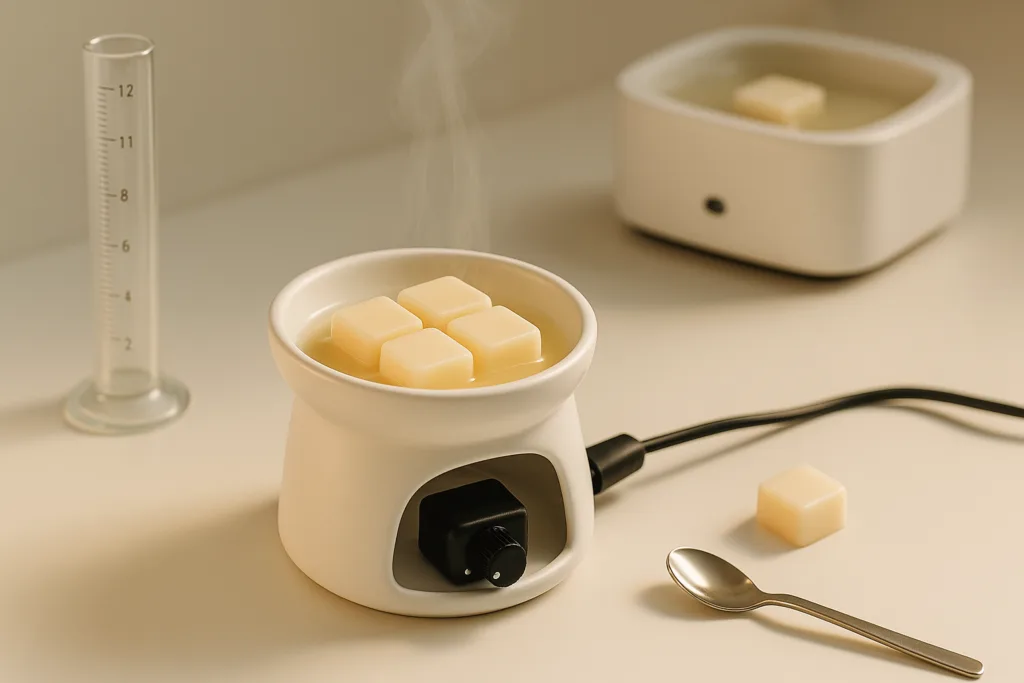
Step 4 — Melt Wax Application Testing (Laboratory Scale)
Fragrance behaves differently in wax than on strips. Therefore, the most appropriate melt wax base is selected.
Common bases include:
- Soy blend
- Coconut blend
- Beeswax enhanced wax
During laboratory melting:
- Heat index is monitored
- Fragrance binding rate is evaluated
- Pool coverage is measured
What matters most:
- Cold throw strength at room temperature
- Performance during melting cycle
Once formula performance is confirmed, a small pilot batch is recommended.
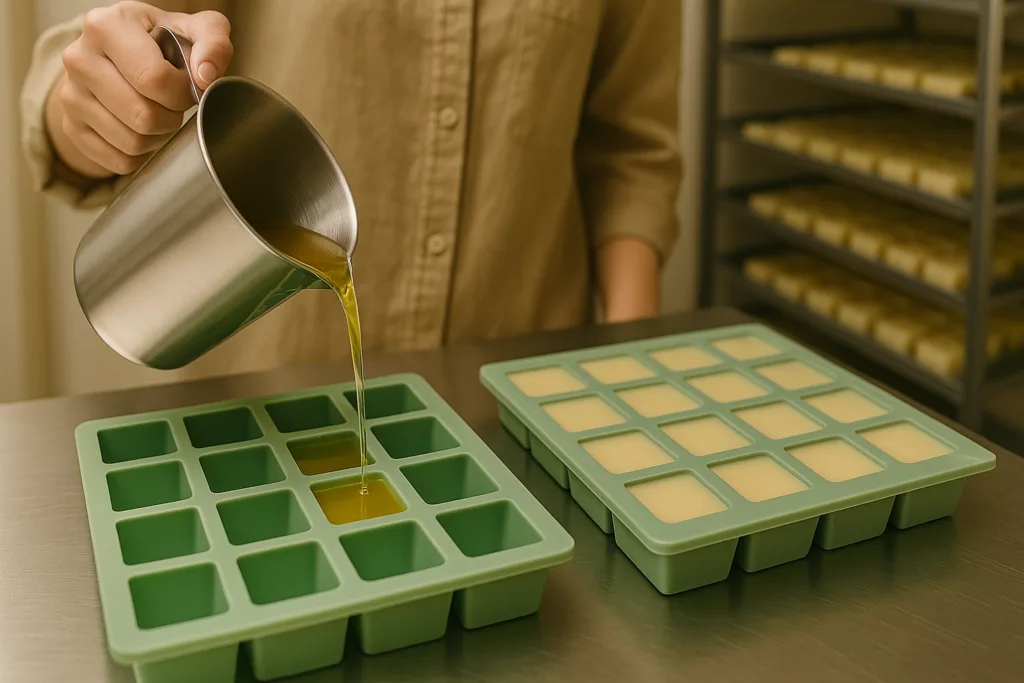
Step 5 — Pilot Batch Production (Typically 2–5 kg)
Pilot batches are the fastest way for retailers to:
- Test sales at physical locations
- Run influencer gifting campaigns
- Validate consumer preference
- Compare scent consistency after curing
Brands commonly run small‑batch pilot tests during:
- Holiday launches
- Small‑batch local markets
- Pre‑launch sampling events
During pilot runs, QC notes include:
- Color uniformity
- Wax clarity
- Solidification smoothness
- Aroma release timing
If standards are achieved consistently, full OEM production follows.
Step 6 — Feedback, Adjustments & Final Confirmation
Feedback often comes from two sources:
- Internal product team sensory scoring
- Real consumer comments from initial test sales
Adjustments usually relate to:
- Increasing mid‑note projection
- Reducing sweetness intensity
- Enhancing wood residue tones
This step ensures alignment between desired brand profile and actual scent experience.
Step 7 — Full Certification and Compliance Preparation
For export to Europe, and partially to the United States, documentation typically includes:
- IFRA statements
- SDS sheets
- CLP labeling data
- GHS hazard identification
- Allergen disclosure
In addition, vegan and cruelty‑free claims increasingly become retail requirements.
High compliance visibility significantly improves wholesale acceptance.
3. How Fragrance Matching Differs Between Melt Wax and Candles
Although many brands assume that fragrance performance is similar across both categories, application science shows notable differences.
Differences in fragrance behavior:
| Property | Melt Wax | Candle |
|---|---|---|
| Aroma release | Faster | Gradual diffusion |
| Fragrance binding sensitivity | Moderate | Higher |
| Performance at low room temps | Strong | Medium |
| Ideal test batch | 2–5 kg | 50 kg+ |
Why melts are used before candle launches
Because melts do not require wick optimization, they allow:
- Faster evaluation cycles
- Reduced production cost
- Lower freight cost for sampling
- Rapid A/B fragrance comparison
Retailers often release melts first, and candles two months later.
4. Technical Factors That Influence Fragrance Accuracy
Some customers assume that matching is easy as long as GC–MS is available. In reality, multiple technical layers affect success.
Key variables include:
1. Flash Point
This determines how components behave when heated.
2. Solubility Compatibility
Some esters cloud wax if not balanced correctly.
3. Fragrance Retention Rate
Measured after full cure.
4. Evaporation Window
Affects both cold and hot throw.
Laboratories use scoring systems such as:
- T‑window release span
- Persistence curve stability
- Top note decay index
These ensure consistency throughout multiple heating cycles.
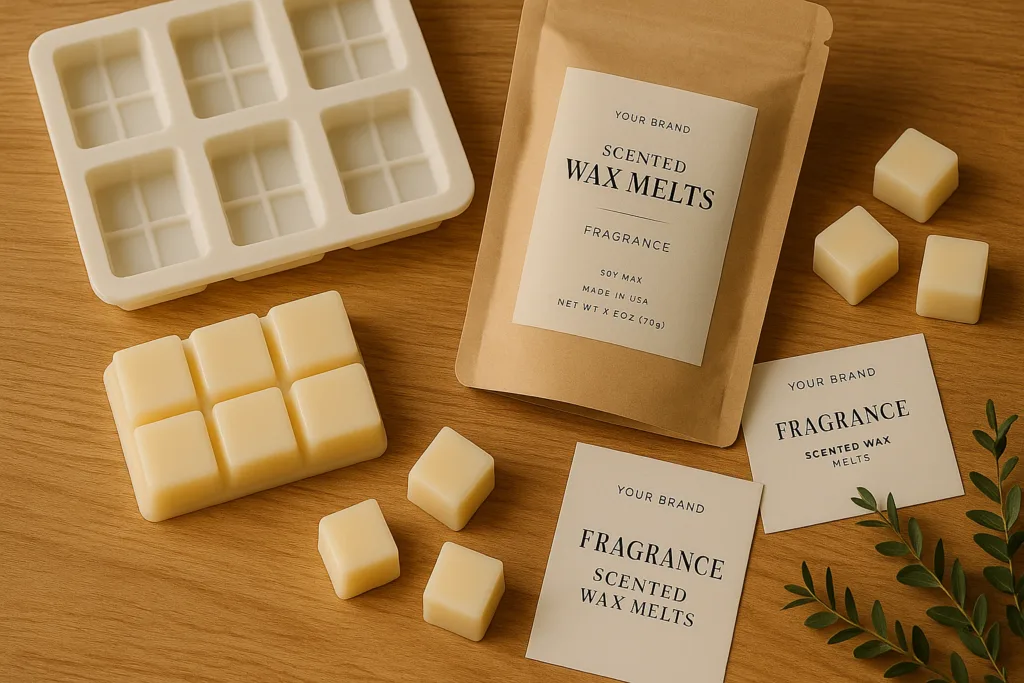
5. Material & Packaging Directions for Melt OEM Programs
OEM deliverables often include:
Base Wax Types:
- Soy melt bar
- Coconut blend pellets
- Beeswax hybrid molds
Mold Shapes:
- Rectangle bar scoring blocks
- Cube tray melts
- Flower mold decorative melts
- Logo‑embossed patterns
Packaging Formats:
- Compostable kraft pouch
- Heat‑sealed PVC clamshell
- Fully printed folding box
These physical formats strengthen brand identity during retail display.
6. Common OEM Scenarios & Real‑World Use Cases
Scenario A — Boutique Retail Launch (Seasonal)
- 2 fragrances developed
- Sold during winter season
- Promotional gifting strategy
Scenario B — Candle Brand Line Extension
- Matching melt version of existing candle scent
- Keeps brand portfolio unified
Scenario C — Business Validation Phase
- Companies launch only melts first
- If sell‑through rate exceeds forecast
- Larger SKU expansion begins
Pilot melt batches provide measurable forecasting accuracy.
7. Evaluation Guidelines for Buyers Testing Pilot Batches
Brand teams often score:
- Room fill within 10 minutes
- Dry scent intensity after cooling
- Diffusion range
- Lingering base tone stability
Shoppers often describe:
- “warm vanilla remains after melting”
- “cedarwood stays even when finished”
- “fresh bergamot noticeable at entrance area”
These qualitative signals give direction for final adjustments.
8. Production & Lead‑Time Timeline Overview
Typical timeline:
| Phase | Duration |
| Requirements validation | 2–3 days |
| Sample testing & GC–MS | 7–14 days |
| Trial formula creation | 10–20 days |
| Pilot batch | 7–15 days |
| Final OEM production | 20–40 days |
Total project cycle ranges 6–10 weeks depending on revision frequency.
9. Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can matching be done without a physical scent sample? Yes, but accuracy is lower without reference.
Q: What is the MOQ for pilot melts? Often 2–5 kg per scent.
Q: How many prototypes do brands see before approving? Usually 2–4 versions.
Q: Does melt wax require labeling compliance? For EU and UK distribution—yes.
Q: What region has the strictest compliance rules? Europe historically has the most transparent labeling requirements.
Conclusion: The Value of a Structured OEM Fragrance System
Developing a custom scent for melt wax products requires analytical expertise, sensory calibration, compliance understanding, and iterative testing. Retailers that invest in a signature fragrance obtain brand differentiation that competitors cannot replicate easily. Melt wax is particularly suitable for early fragrance validation due to low MOQ, fast turnaround, and strong scent performance.
When developed through a structured OEM system—from scent interpretation to pilot production—brands secure more predictable results, enhance retail storytelling, and scale efficiently into candles, body fragrance products, and larger seasonal campaigns.